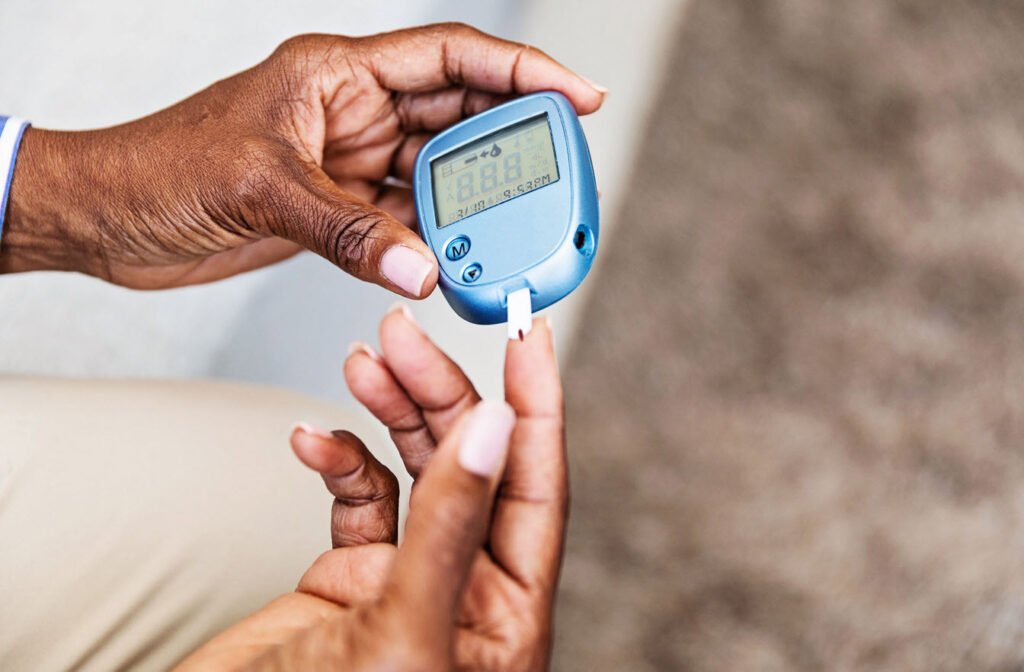
Maintaining healthy glucose levels is essential for overall well-being, as dysregulation can lead to a host of health issues, including obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and more.
The following questions can serve as a self-assessment tool to help you determine whether your glucose levels might be out of balance.
If you find yourself answering “yes” to many of these questions, it may be an indicator that your glucose levels are dysregulated and that you should consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance.
1. Have you been told by a doctor that you need to lose weight?
Weight gain and obesity can be linked to glucose dysregulation, so if a healthcare provider has suggested weight loss, it could be due to concerns about your glucose levels.
2. Are you trying to lose weight but finding it difficult?
Struggling to shed pounds despite your efforts may indicate an underlying glucose issue.
3. Is your waist size (or pant size) above 40 inches if you are a man or above 35 inches if you are a woman?
Research suggests that waist size can be a more reliable predictor of underlying disease than BMI. An increased waist size may be linked to glucose problems.
4. Do you have extreme hunger pangs during the day?
Intense hunger, particularly when it strikes suddenly, could be a sign of glucose imbalances.
5. Do you feel agitated or angry when you are hungry, aka hangry?
Irritability when hungry may be a symptom of blood sugar fluctuations.
6. Do you need to eat every few hours?
Frequent snacking to maintain energy levels might be indicative of glucose instability.
7. Do you feel shaky, lightheaded, or dizzy if meals are delayed?
These symptoms are often associated with low blood sugar and can be a warning sign.
8. Do you crave sweet things?
Intense cravings for sugary foods could be your body’s way of trying to stabilize glucose levels.
9. Do you feel sleepy midmorning or midafternoon or are you tired all the time?
Fatigue and drowsiness, especially after meals, can be related to blood sugar issues.
10. Do you need caffeine to keep you going throughout the day?
Relying heavily on caffeine for energy may suggest glucose instability.
11. Do you have trouble sleeping or wake up with heart palpitations?
Sleep disturbances and heart palpitations can be related to glucose imbalances.
12. Do you have energy crashes where you break out in a sweat or get nauseous?
Sudden energy crashes accompanied by sweating or nausea can be tied to glucose dysregulation.
13. Do you suffer from acne, inflammation, or other skin conditions?
Skin issues can sometimes be associated with imbalanced glucose levels.
14. Do you experience anxiety, depression, or mood disorders?
Mood swings and mental health challenges can be influenced by glucose fluctuations.
15. Do you experience brain fog?
Cognitive difficulties, like brain fog, may be related to glucose issues.
16. Is your mood variable?
Rapid mood changes can be linked to unstable glucose levels.
17. Do you frequently get colds?
A weakened immune system due to glucose imbalances can lead to frequent illnesses.
18. Do you experience acid reflux or gastritis?
Gastrointestinal issues may have connections to glucose regulation.
19. Do you have hormonal imbalances, missed periods, PMS, infertility, or PCOS?
Hormonal disruptions can be associated with glucose problems.
20. Have you ever been told that your glucose levels are elevated?
If you’ve received a diagnosis of elevated glucose levels, it’s crucial to manage and monitor your blood sugar.
21. Do you have insulin resistance?
Insulin resistance is a strong indicator of glucose dysregulation.
22. Do you have prediabetes or type 2 diabetes?
These conditions are directly linked to glucose imbalances.
23. Do you have nonalcoholic fatty liver disease?
This liver condition can be influenced by glucose dysregulation.
24. Do you have heart disease?
Cardiovascular issues can be exacerbated by glucose problems.
25. Do you have difficulty managing gestational diabetes?
Pregnancy-related diabetes can affect glucose levels.
26. Do you have difficulty managing type 1 diabetes?
Maintaining glucose control can be challenging for individuals with type 1 diabetes.
If you find that many of these questions resonate with your experience, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide a thorough evaluation, help you understand the root causes of your glucose issues, and guide you in managing and improving your glucose levels for better overall health.
Remember that early detection and proactive management are key to preventing more severe health conditions associated with glucose dysregulation.