In recent times, the world has faced unprecedented health crises, from the COVID-19 pandemic to emerging infectious diseases. Now, a new threat looms at India’s doorstep: the Mpox (MonkeyPox) virus. The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared a global health emergency, raising concerns about the potential impact and the need for swift action.
What is Mpox?
Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, is a viral illness caused by the Mpox virus, a member of the Orthopoxvirus genus within the Poxviridae family.
First identified in monkeys in 1958, it has now become a significant public health concern for humans.
Zoonotic Diseases: A Bridge Between Humans and Animals
Zoonotic diseases are infections that spread between humans and animals.
- These infections can be caused by various germs, including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi.
- Some zoonotic diseases can be severe and life-threatening, such as rabies, while others may be milder.
The Two Clades of the Mpox Virus
- The Mpox virus exhibits two genetic clades: clade I and clade II.
- The recent outbreak is primarily attributed to clade IIb, which has been spreading globally.
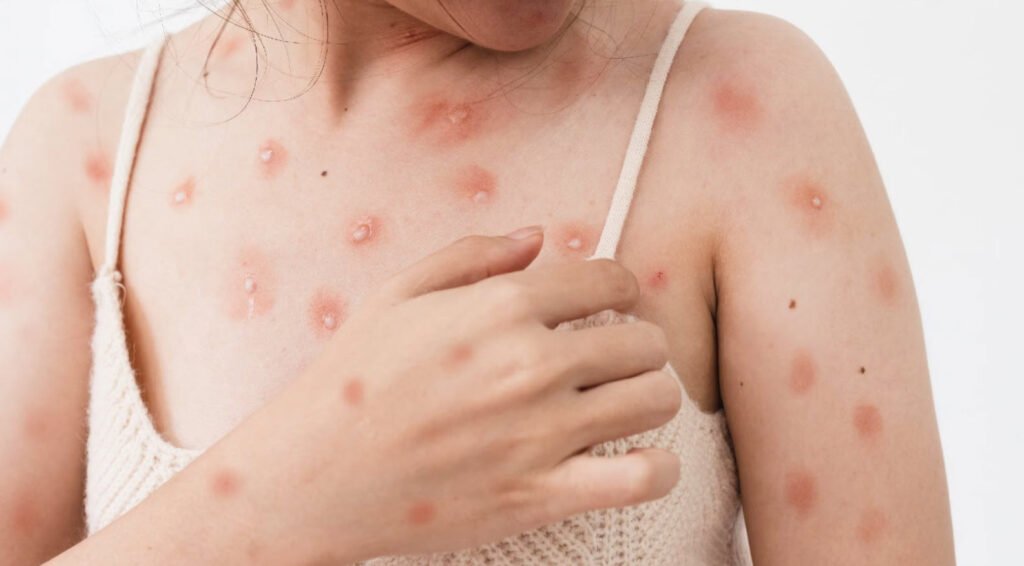
Recognizing Mpox Symptoms
- Common symptoms of Mpox include:
- Skin rash or mucosal lesions
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Back pain
- Swollen lymph nodes
- The rash can persist for 2–4 weeks and may cause discomfort.
How Does Mpox Spread?
- Mpox spreads through direct contact with infectious skin or lesions. Modes of transmission include:
- Face-to-face contact
- Skin-to-skin contact
- Mouth-to-mouth contact
- Mouth-to-skin contact
- Additionally, it can spread through respiratory droplets or contaminated materials like sheets or clothes.
Treatment, Prevention, and Impact
- Treatment: There is no specific antiviral treatment for Mpox. Supportive care is provided to manage symptoms.
- Vaccines and Therapeutics: Vaccines and therapeutics developed for smallpox may be used in certain circumstances.
- Prevention: Key preventive measures include avoiding contact with infected individuals and vaccination for those at risk.
- Impact: The outbreak has already resulted in over 14,000 cases and 500 deaths globally.
- Response: WHO and governments are collaborating to implement a response plan, with an initial funding requirement of $15 million.
Public Health Measures and Ongoing Research
- Public Health Measures: Education, awareness campaigns, and surveillance are crucial to containing the spread of Mpox.
- Current Research: Ongoing research aims to understand the natural reservoir of the virus and develop better diagnostic tests and treatments.
As the world faces this new health emergency, global cooperation and swift action are essential to protect lives and prevent further spread. Let us stay informed, vigilant, and united in our efforts to combat Mpox and safeguard public health .


